Intel’s 18A Processor | A US-Made Comeback
The buzz around the Intel 18A processor is palpable, almost electric. But it’s more than just another chip announcement; it represents a potential turning point a US-made resurgence in the cutthroat world of semiconductor manufacturing. So, why should you, sitting here in India, care about something being cooked up in a US fab? Let’s dive into the ‘why’ behind this comeback, and why it matters globally, not just stateside.
Why the 18A Matters | More Than Just Speed

The implications of Intel’s 18A go way beyond bragging rights about clock speeds and teraflops. It’s about securing a vital piece of the technological puzzle domestic chip production. For decades, manufacturing has largely shifted overseas, creating vulnerabilities in supply chains. And, let’s be honest, a world overly reliant on a single source for crucial technology is a world teetering on the edge of potential disruptions. Remember the chip shortages that plagued industries during the pandemic? The semiconductor industry is now aggressively trying to avoid such incidents in the future. The 18A is Intel’s attempt to bring some of that production back home, increasing stability and security.
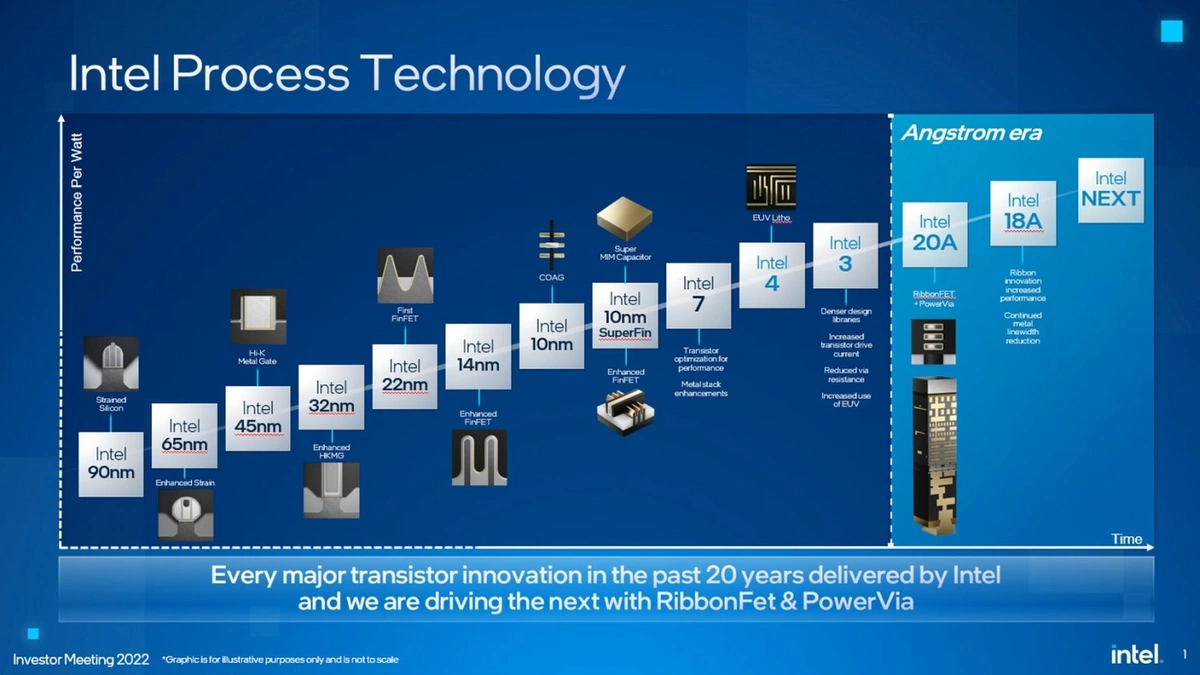
But there’s more! The Intel 18A technology boasts advancements in transistor design and manufacturing processes. We are talking about the RibbonFET, Intel’s implementation of gate-all-around transistors, and PowerVia, for backside power delivery. According to experts, these innovations could lead to significant improvements in performance and power efficiency. Think of it as moving from a congested, pothole-ridden road to a smooth, multi-lane highway. This means faster computing, longer battery life for our devices, and more powerful AI – all impacting us, no matter where we are.
The Geopolitical Chessboard | India’s Position
Here’s the thing: the Intel 18A processor isn’t just about the US. It’s about a global realignment of power. As countries strive for technological independence, India is also making strides in building its own semiconductor ecosystem. This includes incentivizing foreign investment and nurturing domestic talent. Intel’s moves and the success of the 18A could indirectly influence India’s own ambitions, potentially leading to collaborations, technology transfers, and a more robust global chip market. It’s like watching two titans clash, knowing that the ripples will eventually reach your shore.
The competition in the advanced packaging market is heating up, with Intel, TSMC, and Samsung all vying for market leadership. This competition is driving innovation and is expected to benefit the entire industry. Read more about advanced packaging here .
The Technical Deep Dive (Without the Jargon Overload)
Okay, let’s get a little technical, but I promise to keep it relatable. The 18A process node refers to the size of the transistors on the chip 18 Angstroms. Smaller transistors mean more transistors can be packed onto the chip, leading to more processing power. It’s like fitting more apartments into the same building footprint. But it’s not just about size; it’s about how those transistors are built. Intel’s RibbonFET and PowerVia technologies are crucial here, allowing for better current flow and reduced resistance. I initially thought this was all just marketing hype, but then I looked at the engineering papers, and the potential efficiency gains are genuinely impressive. It’s one thing to shrink things; it’s another to shrink them and make them better.
What fascinates me is the extreme ultraviolet lithography (EUV) used in the manufacturing process. This complex process uses light with extremely short wavelengths to etch incredibly fine details on the silicon wafer. Think of it as using a super-precise laser to carve a masterpiece. It’s an incredibly challenging technology, and mastering it is key to producing advanced chips like the 18A. India’s efforts to attract semiconductor manufacturing could benefit from these advancements.
The Road Ahead | Challenges and Opportunities
Let’s be honest: the semiconductor manufacturing game is not for the faint of heart. Intel faces significant challenges in bringing the 18A to mass production. Competition from TSMC and Samsung is fierce, and the technological hurdles are immense. But the potential rewards regaining manufacturing leadership and securing a vital supply chain are worth the effort. For India, the success of the 18A could open doors for collaboration, technology transfer, and a more diverse and resilient global chip market. It’s like watching a high-stakes poker game – you might not be playing, but the outcome affects everyone at the table. The development of the Intel foundry services is going to benefit many companies.
By the way, have you checked out the new iPhone prices in India ? It is interesting how the prices vary.
And there’s this: the focus on US-based manufacturing is creating jobs and stimulating economic growth. This has a knock-on effect, encouraging further investment in research and development. In the long run, this could lead to even more groundbreaking innovations, further solidifying the US’s position in the tech world. It’s a virtuous cycle innovation leading to growth, leading to more innovation. And that’s something everyone can benefit from. Also, consider the potential impact on the artificial intelligence (AI) sector, which heavily relies on advanced processors.
The Human Angle | Why Should You Care?
So, why should you care about the Intel 18A? Because it’s about more than just chips. It’s about the future of technology, the security of supply chains, and the geopolitical landscape. It’s about innovation, competition, and the potential for a more robust and resilient global economy. It’s about the technology that powers our phones, our cars, our hospitals, and our homes. It’s about ensuring that we have access to the technology we need, when we need it. And that, my friend, affects all of us, no matter where we live. Don’t forget to read about Intel’s Panther Lake . You will find it interesting.
The success of the 18A is intertwined with the global push for greater technological self-sufficiency. India, with its growing economy and ambitious technological goals, stands to gain significantly from a more diverse and resilient chip market. The processor will be key to edge computing applications.
FAQ
What exactly is the Intel 18A processor?
It’s Intel’s upcoming processor built on their 18A process node, featuring advanced transistor technology (RibbonFET) and backside power delivery (PowerVia). It aims to deliver significant improvements in performance and power efficiency.
Why is everyone making such a big deal about US-based manufacturing?
It’s about reducing reliance on a single source for critical technology, strengthening supply chains, and boosting domestic job creation.
How does this affect India’s tech ambitions?
A successful 18A could open doors for collaboration, technology transfer, and a more diverse global chip market, benefiting India’s own semiconductor initiatives.
When will we see the Intel 18A processor in actual products?
Intel is targeting 2025 for production. So, keep an eye out for announcements in the coming months.
Is the 18A only for high-end applications?
While it’s initially aimed at high-performance computing, the technologies developed for the 18A could eventually trickle down to other applications.
What are the main competitors to Intel’s 18A?
TSMC and Samsung are the main competitors, both developing their own advanced manufacturing processes.