Ancient Comet Predating the Sun Observed by Mars Spacecraft
Okay, so you’ve heard about a comet . Big deal, right? We see them every few years. But this one? This one’s different. This isn’t your run-of-the-mill icy space rock; this ancient celestial wanderer, observed by a Mars spacecraft, is like finding a fossil that rewrites the entire history book. And what fascinates me is that it is even predating the sun. Let’s dive in, shall we?
Why This Comet Matters | Rewriting the Solar System’s Story

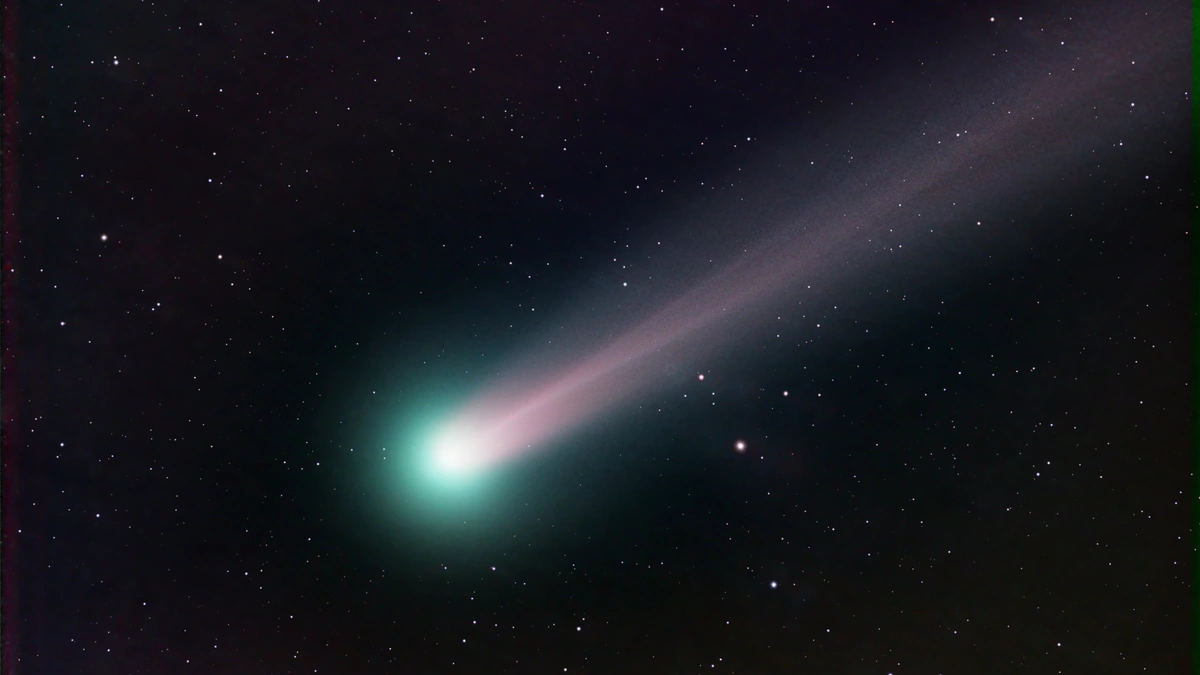
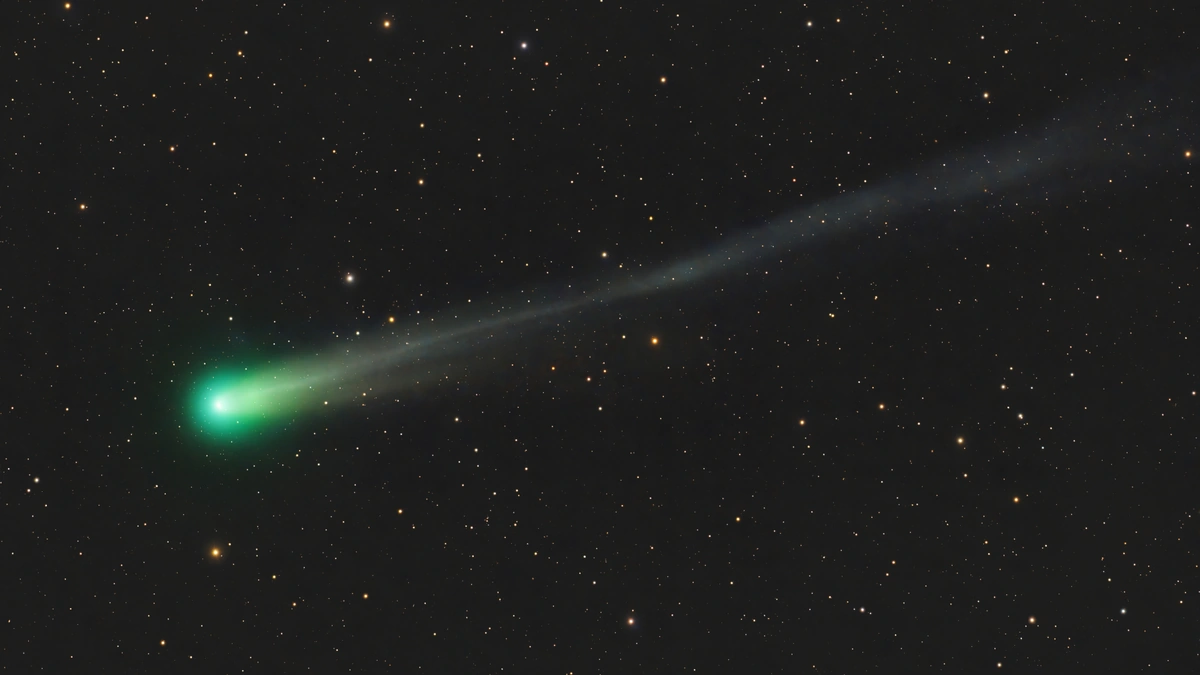
Here’s the thing: most comets we see are leftovers from the formation of our solar system – icy bodies that got kicked out to the fringes and occasionally swing back in. They’re like the crumbs left after baking a cosmic cake. But this particular Oort cloud comet , observed by instruments aboard a Mars spacecraft (specifically, the Mars Express), is believed to be older than the Sun itself. Think about that for a second. It’s like finding a brick from a house that was built before the land existed. As per NASA , this finding challenges our current understanding of how the solar system came together. This isn’t just about astronomy; it’s about cosmology, about understanding the very origins of everything around us.
So, how does spotting a comet near Mars, help us understand the solar system better? Well, the data collected provides valuable insights into the composition and conditions of the early solar system. By studying the comet’s chemical makeup, scientists can infer the building blocks that were present during the solar system’s infancy. This then allows for the creation of a more accurate timeline for the evolution of planets and other celestial bodies.
The ‘How’ of Observation | A Martian Perspective
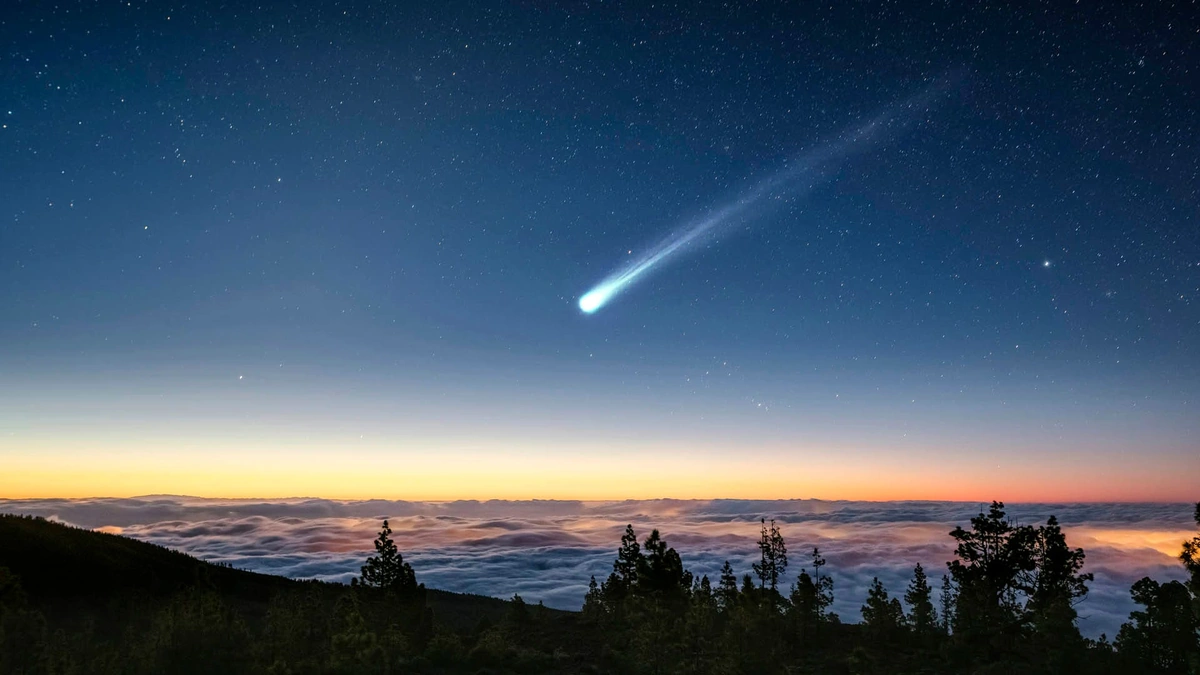
The Mars Express spacecraft, equipped with sophisticated cameras and spectrometers, played a crucial role in observing this ancient comet. Orbiting the Red Planet, it offered a unique vantage point, away from Earth’s atmospheric interference. But, it wasn’t like they were waiting for a sungrazing comet . The spacecraft just happened to be in the right place at the right time, which is sometimes how science works – a bit of luck mixed with a lot of preparation.
What really helped was the spacecraft’s ability to analyze the comet’s coma and tail. The coma is the hazy atmosphere that forms around the nucleus of a comet as it approaches the Sun, and the tail is the stream of gas and dust that extends away from the comet, pushed by solar wind and radiation. By studying these features, scientists were able to determine the comet’s composition and origin. A common mistake is only believing what we are directly told, which is why such observations are vital in helping us form better judgements on the topic.
Decoding the Comet’s Composition | A Glimpse into the Past
What fascinates me the most is the comet’s composition. What did they find? If this comet predates the sun, then it should be made of elements and compounds from an even earlier star. These icy bodies contain pristine material – a snapshot of the conditions that existed billions of years ago. Analyzing the comet’s dust and gas reveals the presence of various elements and molecules, including water ice, carbon dioxide, and organic compounds. These observations help scientists understand the building blocks of planets and life itself. Scientists are very curious about what this comet holds.
But, let’s be honest, it’s not as simple as just looking at it. Scientists use complex techniques like spectroscopy to break down the light emitted by the comet into its constituent wavelengths. This provides a fingerprint of the elements and molecules present, allowing them to identify the comet’s chemical makeup. According to the Planetary Society , one challenge is that these comets are often faint and distant, making observations difficult.
The Emotional Angle | Connecting with Our Cosmic Origins
That moment of awe when you realize you’re looking at something older than the Sun – it’s a profound experience. Thinking about an interstellar object gives you a sense of how small we really are in the grand scheme of things. It connects us to the very beginnings of the universe, to the processes that created the stars and planets, and ultimately, us. It’s humbling and inspiring all at once. Space is so vast and beautiful , and things such as this should remind us of how amazing it is.
And so, we must question, what does it mean? It means that the story of our solar system is more complex and nuanced than we previously thought. It suggests that some of the building blocks of planets and life may have originated from even earlier generations of stars. It’s a reminder that we are all connected to the cosmos, to the ebb and flow of matter and energy that has shaped the universe for billions of years. The implications are huge and there is so much to discover.
Future Implications | What’s Next in Comet Research?
So, what’s next? The discovery of this ancient comet opens up new avenues for research. Future missions could be designed to directly sample cometary material, bringing it back to Earth for detailed analysis. Advanced telescopes, both on the ground and in space, will continue to monitor comets, providing a more comprehensive understanding of their behavior and composition. Plus, who knows what secrets a long-period comet could be hiding.
But it’s not just about new technology. It’s also about re-examining existing data with fresh eyes, using new analytical techniques to uncover hidden patterns and insights. It’s about collaboration, bringing together experts from different fields to share their knowledge and perspectives. And it’s about curiosity, that fundamental human drive to explore, to understand, and to push the boundaries of what we know. The more we find out, the more we have to learn.
And you might ask, could these comets offer resources? It’s not out of the question! Look at recent achievements and ask yourself, is it really impossible? Who knows!
FAQ About Comets
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a comet made of?
Comets are often described as “dirty snowballs.” They are primarily composed of ice (water, carbon dioxide, etc.), dust, and small rocky particles.
Where do comets come from?
Most comets originate from either the Kuiper Belt, a region beyond Neptune, or the Oort Cloud, a vast spherical region much farther out.
How often do we see comets?
The frequency varies. Some comets have short orbital periods and appear regularly, while others have extremely long periods and are only seen once.
Can a comet hit Earth?
Yes, it’s possible, although the chances of a major impact are very low. Scientists are constantly monitoring near-Earth objects to assess any potential risks.
Are comets dangerous?
While the probability of a catastrophic impact is small, comets pose a theoretical threat. Space agencies around the world monitor potentially hazardous objects and are developing strategies for planetary defense.
So, the next time you see a comet streaking across the night sky, take a moment to appreciate its cosmic significance. It’s a messenger from the past, a window into the origins of our solar system, and a reminder of the vast, awe-inspiring universe we inhabit. It’s one of those celestial objects that puts things into perspective, don’t you think?