Decoding PPP | Why It Matters Now More Than Ever
PPP. You’ve probably heard the term floating around, especially if you’re involved in finance, infrastructure, or government projects. But let’s be honest it often gets glossed over as just another acronym. What fascinates me is how much this seemingly simple concept shapes the world around us, from the roads we drive on to the power plants that keep our lights on. And in India, with its massive development needs and ambitious growth targets, understanding PPP is crucial.
So, what is PPP? It stands for Public-Private Partnership. But it’s more than just a fancy term. It’s a contractual agreement between a public agency (federal, state, or local) and a private sector entity. The goal? To deliver a project or service traditionally handled by the public sector. Think of it as a marriage of convenience (and necessity) where each partner brings unique strengths to the table.
The “Why” Behind PPP | Bridging the Infrastructure Gap
Here’s the thing: governments often struggle with massive infrastructure projects due to budget constraints, lack of technical expertise, or bureaucratic delays. Private companies, on the other hand, are usually more efficient, innovative, and have access to capital. The beauty of PPP is that it allows governments to leverage private sector resources to build and maintain essential infrastructure. This is especially critical in a country like India, where the infrastructure deficit is a major bottleneck to economic growth. According to a report by Invest India , the country needs trillions of dollars in investment to meet its infrastructure needs.
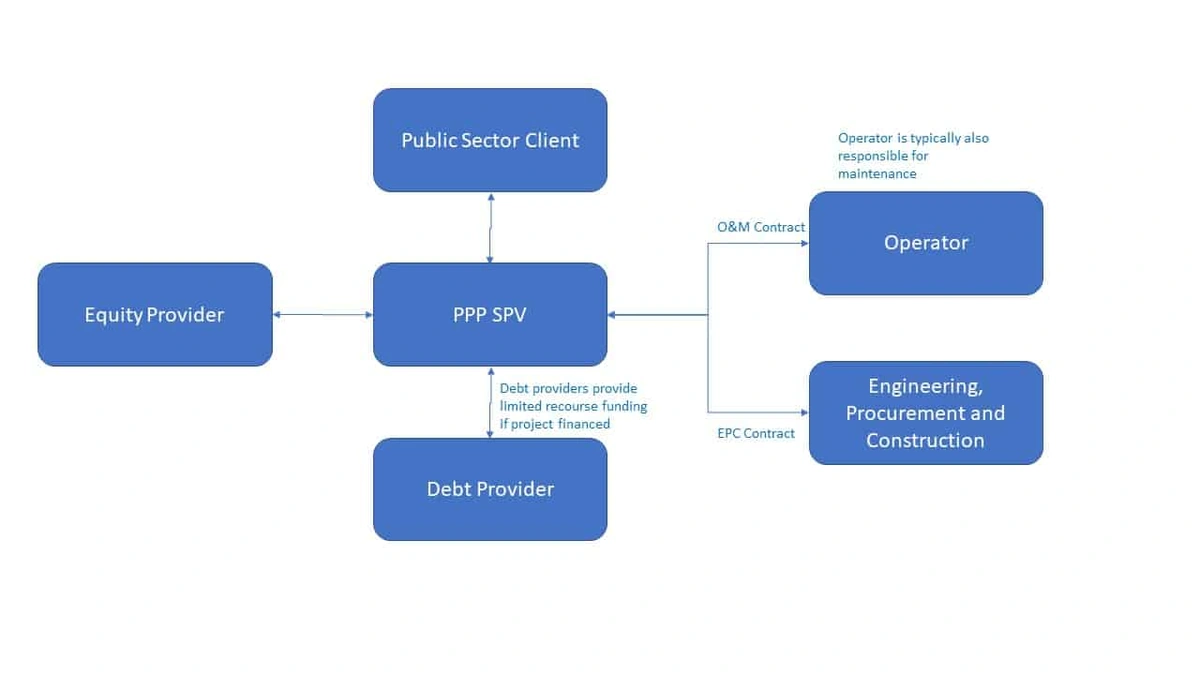
But it’s not a free lunch. The private sector is involved to make a profit. So, how does it work? Typically, the private company invests its own capital, designs, builds, and operates the project. In return, the government (or the users of the infrastructure) pay the company over a specified period. This can be through user fees (like tolls on a highway) or government payments (based on performance). A common mistake I see is that people think PPPs are simply privatization. They’re not. The government retains ownership of the asset; the private sector merely manages it for a set period.
How PPP Works in Practice | A Step-by-Step Guide
Let’s break down the process involved in a typical PPP project. It’s not as straightforward as building a house, but understanding the steps can help you grasp the complexities involved:
- Identification: The government identifies a need for a specific project, such as a new highway, a water treatment plant, or a hospital.
- Feasibility Study: A detailed study is conducted to assess the project’s viability. This includes analyzing the technical, financial, and environmental aspects.
- Tendering Process: The government invites private companies to submit bids for the project. This process is usually highly competitive.
- Selection of Partner: The government evaluates the bids and selects the company that offers the best value for money.
- Contract Negotiation: The government and the selected company negotiate the terms of the PPP agreement. This is a crucial step, as the agreement will govern the relationship between the parties for the entire duration of the project.
- Construction: The private company designs and builds the project.
- Operation and Maintenance: The private company operates and maintains the project for the agreed-upon period.
- Transfer: At the end of the contract period, the project is transferred back to the government.
And, you should keep in mind this is a general outline. Different projects may have variations in these steps. The key is that the government and the private company work together throughout the entire lifecycle of the project.
But even with a well-defined process, PPPs face challenges. Political interference, regulatory hurdles, and financing difficulties can all derail a project. This is why it’s essential to have a strong legal and regulatory framework in place to support PPPs.
The Emotional Angle | Overcoming Skepticism and Building Trust
Let’s be honest: PPPs often face public skepticism. People worry about private companies exploiting public resources or cutting corners to maximize profits. And those fears are valid, which underscores the importance of transparency and accountability. A common criticism I see is that these projects are not properly vetted. To foster trust, the government must ensure that PPP agreements are fair, transparent, and benefit the public. This is about more than just economics; it’s about building confidence in the system.
What fascinates me is how successfully implemented PPPs can transform communities. They can bring better infrastructure, create jobs, and improve the quality of life. But it requires a shift in mindset from viewing the private sector as an adversary to seeing it as a partner in development. This requires effective communication, stakeholder engagement, and a willingness to address concerns.
The Future of PPP in India | Opportunities and Challenges
So, what does the future hold for PPP in India? The potential is enormous. As the country continues to grow and urbanize, the demand for infrastructure will only increase. PPPs can play a vital role in meeting this demand. The government has set ambitious targets for infrastructure development, and PPPs are expected to contribute significantly to achieving these goals. Internal Link: Property Law
But there are also challenges. One of the biggest is the need to improve the regulatory framework. PPP projects often get bogged down in bureaucratic delays and regulatory uncertainty. The government needs to streamline the approval process and create a more predictable investment environment. According to the World Bank, India ranks relatively low in terms of ease of doing business, and this impacts the attractiveness of PPP projects.
Another challenge is the need to develop innovative financing mechanisms. PPP projects often require significant upfront investment, and financing can be a major constraint. The government needs to explore new ways to attract private capital, such as infrastructure bonds and credit enhancement mechanisms. The one thing you absolutely must consider is the long-term sustainability of the project. It’s not enough to simply build infrastructure; you also need to ensure that it’s properly maintained and operated for the long term.
Real-World Examples | Success Stories and Lessons Learned
Let’s look at some real-world examples of PPP projects in India. One notable example is the Delhi Metro, which has transformed public transportation in the capital city. The Delhi Metro is a joint venture between the central government and the Delhi government, with private companies involved in construction and operation. The project has been widely praised for its efficiency, cleanliness, and safety. But the metro wasn’t built overnight. It involved years of planning, coordination, and overcoming numerous challenges. A common mistake I see is that people underestimate the complexity of these projects. But when done right, the results can be transformative.
Another example is the Mumbai Trans Harbour Sea Link, which will connect Mumbai with Navi Mumbai. This project is being implemented on a PPP basis and is expected to reduce travel time significantly. The link will be the longest sea bridge in India and is expected to boost economic activity in the region. But these big, flashy projects often overshadow smaller, but equally important, PPPs in sectors like water, sanitation, and healthcare. It’s these everyday projects that often have the biggest impact on people’s lives. Internal Link: Stock Market
FAQ
What exactly is a Public-Private Partnership (PPP)?
It’s a collaboration where a government and a private company team up to deliver a service or project, like a road or utility, that the government traditionally handles.
Why would a government choose a PPP model?
Often due to budget limitations, needing private sector efficiency and innovation, or to share risks on large infrastructure projects.
What are the main concerns people have about PPPs?
Skepticism often arises around transparency, whether the deal truly benefits the public, and if the private company might prioritize profit over service quality.
Are PPP projects always successful?
No. Projects may face failure due to regulatory hurdles, funding problems, or improper contract negotiation. Therefore, success is not always guaranteed.
What happens to a PPP project at the end of the contract?
Typically, ownership and operation are transferred back to the government, ensuring the public retains long-term control of the asset.
What fascinates me about PPPs is that they’re not just about building infrastructure; they’re about building partnerships. They’re about finding innovative ways to address the challenges facing our society. And while they’re not a silver bullet, they can be a powerful tool for driving economic growth and improving the quality of life for all. So, the next time you hear about a PPP project, take a moment to understand the deeper implications. It’s not just another acronym; it’s a reflection of our collective effort to build a better future. The PPP model is an important part of our future, whether we realize it or not.