Peritoneal Dialysis | An Untapped Answer to India’s Kidney Disease Crisis
Let’s be honest, when we hear about kidney disease , the immediate image that pops into our heads is often of long, grueling hours spent in a dialysis center. But what if I told you there’s a treatment option that’s not only effective but also allows patients to lead a far more flexible and independent life? I am talking about peritoneal dialysis . For India, where access to healthcare can be a challenge, this could be a game-changer.
The Silent Epidemic | Why India Needs More Options
Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) is a growing problem in India, and the numbers are frankly staggering. It’s not just a health issue; it’s a socio-economic one. Think about the lost productivity, the strain on families, and the overwhelming burden on our healthcare system. The usual hemodialysis, while life-saving, requires frequent visits to a dialysis center, which can be difficult for people in rural areas or those with mobility issues.
What fascinates me is why peritoneal dialysis isn’t more widely adopted. One reason could be a lack of awareness among patients and even some healthcare professionals. Another might be concerns about the initial training and the perceived complexity of the procedure. But, and this is a big but, these concerns are often outweighed by the benefits it offers, which include increased flexibility, fewer dietary restrictions, and potentially better preservation of residual kidney function. The thing is, it improves the quality of life .
Peritoneal Dialysis | Your Guide to a Flexible Future
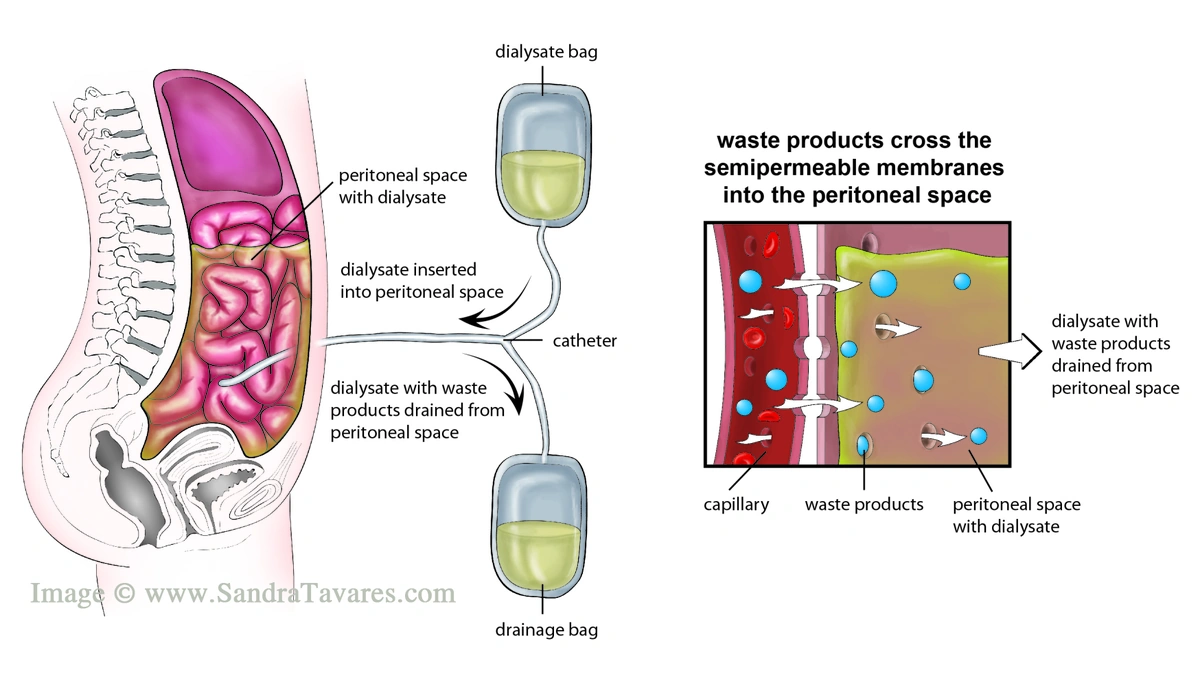
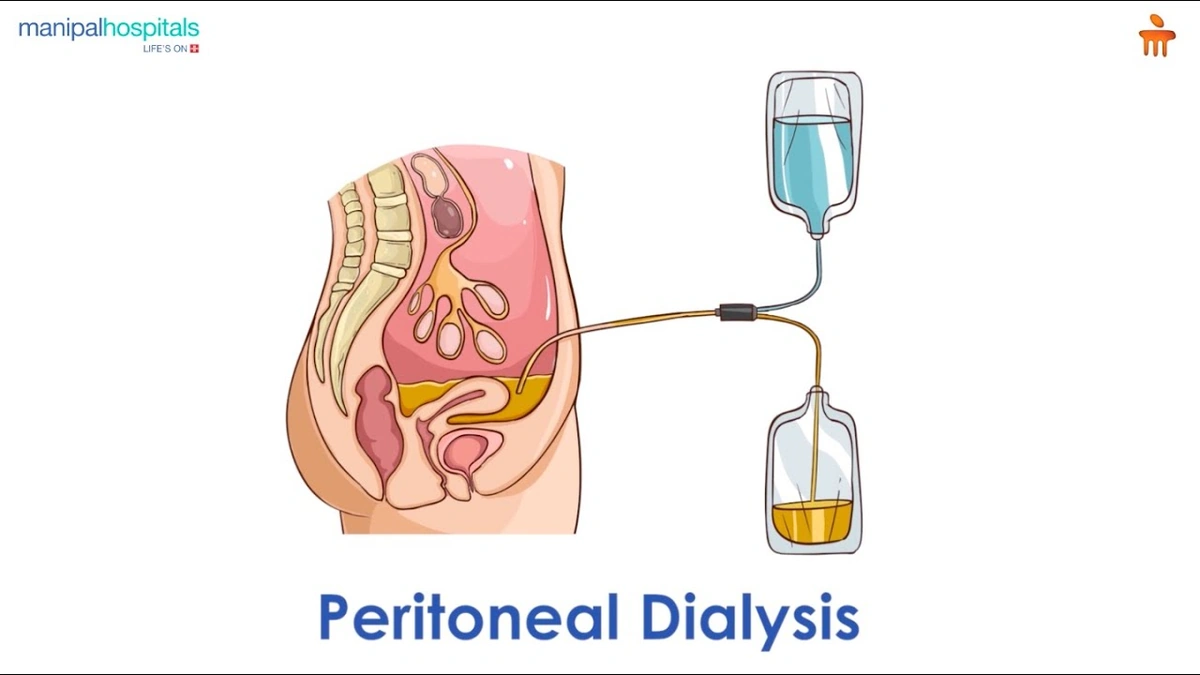
So, how does peritoneal dialysis (PD) actually work? Well, in simple terms, it uses the lining of your abdomen, the peritoneum, as a natural filter. A catheter is placed in your abdomen, and a special solution called dialysate is introduced. This solution draws waste products and excess fluid from your blood across the peritoneal membrane. After a few hours, the solution is drained, and fresh solution is instilled. This process, known as an exchange, can be done at home, at work, or even while traveling.
Let’s break down the two main types of peritoneal dialysis procedures :
- Continuous Ambulatory Peritoneal Dialysis (CAPD): This is a manual process where you perform exchanges throughout the day, typically four to five times. No machine is required, giving you maximum freedom.
- Automated Peritoneal Dialysis (APD): This uses a machine called a cycler to perform exchanges while you sleep. This can be particularly appealing to those who work or have other daytime commitments.
The choice between CAPD and APD depends on your individual needs and preferences. A common mistake I see people make is not thoroughly discussing their lifestyle with their nephrologist to determine the best fit. Don’t be afraid to ask questions and explore all your options. Remember, this is about finding a treatment that works for you.
Addressing the Concerns | Debunking Myths About Peritoneal Dialysis
Now, let’s address some common concerns about peritoneal dialysis. One of the biggest is the risk of infection, specifically peritonitis. Yes, infection is a possibility, but with proper training and adherence to sterile techniques, the risk can be minimized. Hospitals provide comprehensive training to patients and their families on how to perform exchanges safely and effectively.
Another concern is the initial cost of setting up PD at home. While there is an initial investment, the long-term costs may be lower compared to hemodialysis due to fewer hospital visits. What fascinates me is the potential for local manufacturing of dialysate solutions in India, which could significantly reduce costs and improve accessibility. I initially thought this was straightforward, but then I realized the supply chain logistics is very complex.
But the benefits should be considered when evaluating its effectiveness as an alternative to hemodialysis centers . Ultimately, consulting your doctor is the right way to determine the best course of treatment.
The Indian Context | Tailoring Peritoneal Dialysis for Success
Here’s the thing: implementing peritoneal dialysis successfully in India requires a tailored approach. We need to consider factors like patient education, access to clean water, and the availability of trained healthcare professionals in rural areas. Telemedicine and mobile health technologies can play a crucial role in providing remote monitoring and support to patients on PD.
What fascinates me is the potential for community-based programs to promote awareness and provide support to PD patients. Imagine a network of trained community health workers who can visit patients at home, provide guidance, and address any concerns they may have. This could be a game-changer in improving adherence and outcomes, and promoting home kidney treatment . But this requires investment in training and infrastructure.
Looking Ahead | The Future of Kidney Care in India
The future of kidney care in India lies in a multi-pronged approach that includes prevention, early detection, and a wider adoption of peritoneal dialysis. We need to invest in public health campaigns to raise awareness about risk factors for CKD, such as diabetes and hypertension. Early screening programs can help identify individuals at risk and initiate timely interventions. And yes, of course access to affordable medication is an integral element to treating kidney disease.
So, the next time you hear about kidney disease, remember that peritoneal dialysis offers a beacon of hope – a chance for patients to reclaim their lives, maintain their independence, and participate fully in their communities. It’s time to tap into this untapped resource and transform the landscape of kidney care in India, while also working on preventing kidney failure.
FAQ Section
Frequently Asked Questions
Is peritoneal dialysis painful?
No, the process itself is not usually painful. Some people may experience mild discomfort when the catheter is inserted initially, but this usually subsides quickly. Proper catheter care is essential to prevent infection.
Can I travel while on peritoneal dialysis?
Yes, one of the great advantages of PD is that it allows you to travel. You’ll need to plan ahead and ensure you have an adequate supply of dialysate and other supplies. It also means having to plan ahead, to ensure you don’t encounter an emergency situation during any travels you may have .
What are the dietary restrictions for peritoneal dialysis?
The dietary restrictions are generally less strict compared to hemodialysis. You may need to limit your intake of sodium, potassium, and phosphorus, but your dietician will provide personalized guidance. A nephrologist will ultimately decide your dietary limitations.
How long can I stay on peritoneal dialysis?
You can stay on PD for many years, as long as it continues to be effective and well-tolerated. However, some people may eventually need to switch to hemodialysis or consider kidney transplantation. In either case, the process of determining any kind of treatment is between you and your medical team.
What if I forgot my application number?
Forgetting your application number can happen, but don’t panic! The best course of action is to visit the official NTA website (if this is related to an exam) and look for the “Forgot Application Number” link. You’ll likely need to provide some personal details like your name, date of birth, and registered email/phone number to retrieve it. Double-check the details you enter to ensure they match what you used during registration. If you’re still unable to recover it, reach out to the NTA helpdesk immediately.