Naked Mole-Rat DNA Repair | A Key to Human Longevity?
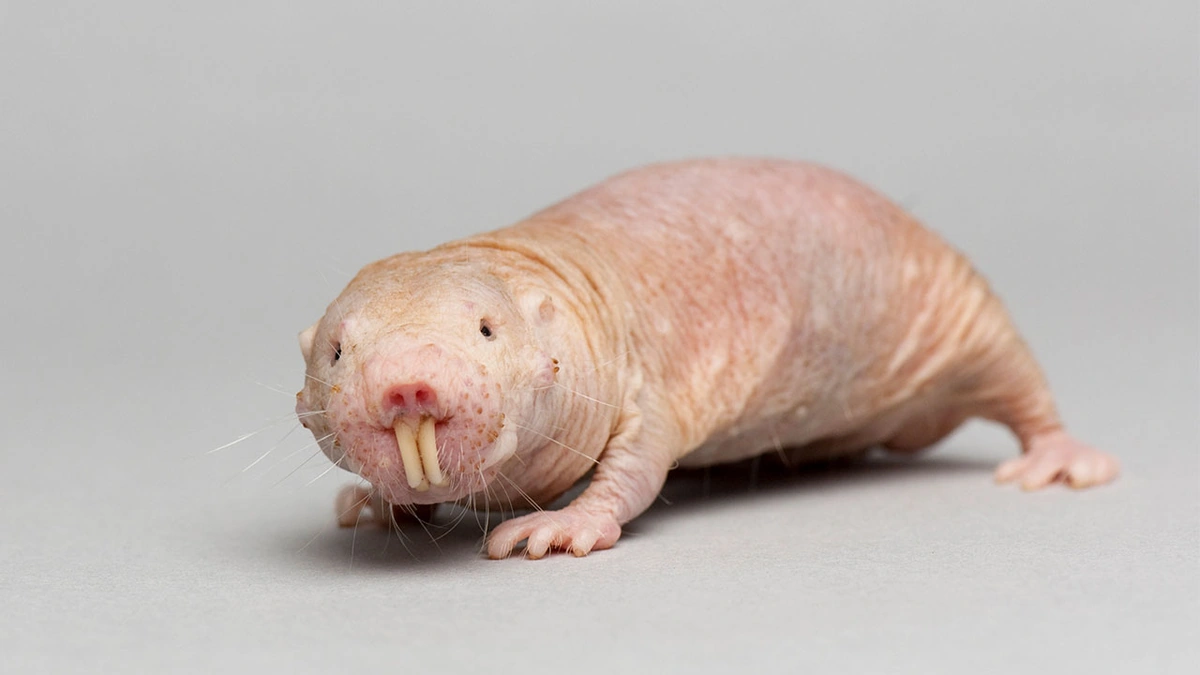
Okay, let’s be real. We all want to live longer, right? But what if the secret wasn’t some fancy new pill or extreme diet, but something… furless and wrinkly? I’m talking about the naked mole-rat. Yes, those bizarre, subterranean creatures are grabbing headlines, and for good reason. The fascinating thing about these animals is their remarkable resistance to age-related diseases, especially cancer. This brings us to a tantalizing question: could understanding naked mole-rat longevity unlock the secrets to extending human lifespan?
The “Why” | What Makes Naked Mole-Rats So Special?
So, what’s the deal? Why are these little guys living so long – often over 30 years – when mice of similar size barely make it past three? Here’s the thing: it all boils down to their extraordinary DNA repair mechanisms. Scientists have discovered that naked mole-rats possess unique genes and proteins that efficiently detect and fix DNA damage, which is a major contributor to aging and cancer. But , it gets even wilder. Their cells are also incredibly resistant to oxidative stress, another key player in the aging process.
Think of it like this: our DNA is constantly under attack from various sources – radiation, pollution, even just the normal metabolic processes in our bodies. These attacks cause damage, and if that damage isn’t repaired, it can lead to mutations, which can then lead to cancer or other age-related diseases. Naked mole-rats, however, have a super-efficient repair crew working 24/7 to keep their DNA in tip-top shape. This superior DNA repair process is due to several factors, including higher levels of certain repair enzymes and a unique version of the hyaluronan molecule, which prevents cancer cells from forming.
The “How” | Naked Mole-Rat DNA Repair in Detail
Let’s dive a little deeper into the “how.” Researchers have identified several key differences in the DNA repair pathways of naked mole-rats compared to other mammals. One crucial difference lies in the efficiency of their nucleotide excision repair (NER) pathway. This pathway is responsible for removing bulky DNA lesions, such as those caused by UV radiation. Naked mole-rats have a much faster and more accurate NER pathway, allowing them to quickly fix damaged DNA before it can cause problems. Additionally, they exhibit enhanced base excision repair (BER), which targets smaller DNA lesions caused by oxidation and alkylation. According to Wikipedia , these enhanced repair mechanisms are crucial for their longevity and cancer resistance.
Another important factor is the presence of high molecular weight hyaluronan (HMW-HA) in their tissues. HMW-HA is a type of polysaccharide that is normally found in the extracellular matrix. In naked mole-rats, HMW-HA has been shown to have potent anti-cancer properties. It works by preventing cells from clumping together and forming tumors. What fascinates me is how this single molecule can have such a profound impact on cancer development. It also modulates the inflammatory response, preventing age-related inflammation, a key driver of aging.
The Emotional Angle | Hope for Human Longevity
Now, I know what you’re thinking: “That’s great for naked mole-rats, but what about me?” Well, here’s where the hope comes in. Scientists are actively studying these unique DNA repair mechanisms to see if they can be translated into human therapies. Imagine a future where we could boost our own DNA repair capabilities, effectively slowing down the aging process and preventing age-related diseases like cancer, Alzheimer’s, and heart disease. It sounds like science fiction, but the research is already underway.
Researchers are exploring several avenues, including gene therapy to introduce naked mole-rat DNA repair genes into human cells, as well as developing drugs that can mimic the effects of HMW-HA. A common mistake I see people make is dismissing this research as too far-fetched. But honestly, the potential benefits are enormous. The implications of this research for understanding cancer resistance are far-reaching.
What’s Next? The Future of Longevity Research
So, what are the next steps? Well, scientists are continuing to unravel the mysteries of naked mole-rat DNA repair, identifying new genes and proteins involved in their remarkable longevity. They are also working on developing new technologies to study DNA repair in human cells, with the goal of identifying targets for therapeutic intervention. We can also look at proteostasis maintenance which is crucial for cell longevity. Scientists are exploring a range of factors that contribute to aging.
One promising area of research is the development of senolytic drugs, which target and eliminate senescent cells – cells that have stopped dividing and accumulate with age, contributing to inflammation and tissue damage. By selectively removing these cells, scientists hope to rejuvenate tissues and organs, effectively slowing down the aging process. Naked mole-rats also exhibit a lower rate of cellular senescence, a key factor in their longevity.
It’s important to note that, while the research is promising, we’re still in the early stages. There are many challenges to overcome before we can translate these findings into effective human therapies. But the potential rewards are so great that it’s definitely worth pursuing. The study of naked mole-rat genetics is providing insights into human health. The more we look the more we are astonished with the exceptionally long telomeres found in naked mole-rats.
Conclusion | A Wrinkly Key to a Longer Life?
The naked mole-rat, that seemingly insignificant creature, might just hold the key to a longer, healthier life for us all. Their extraordinary DNA repair mechanisms offer a tantalizing glimpse into the possibilities of slowing down the aging process and preventing age-related diseases. While there’s still much to learn, the research is progressing rapidly, and the potential benefits are immense. This research has helped us understand the crucial role of DNA damage response pathways in longevity and cancer resistance. I am initially thought this was straightforward, but then I realized that there were more factors.
So, the next time you see a picture of a naked mole-rat, don’t just think of it as a bizarre, wrinkly creature. Think of it as a symbol of hope – a reminder that the secrets to a longer, healthier life might be hidden in the most unexpected places.
Hopefully this research also helps us to understand other aspects of their health like their low metabolic rate and its impacts.
FAQ
What exactly is DNA repair?
DNA repair is a collection of processes by which a cell identifies and corrects damage to the DNA molecules that encode its genome. This is vital for maintaining genomic integrity and preventing mutations.
How do naked mole-rats repair DNA so efficiently?
Naked mole-rats have enhanced DNA repair pathways, including more efficient nucleotide excision repair (NER) and base excision repair (BER). They also possess high molecular weight hyaluronan (HMW-HA), which has anti-cancer properties.
Can we use naked mole-rat DNA to extend human lifespan?
Scientists are exploring the possibility of using gene therapy to introduce naked mole-rat DNA repair genes into human cells. However, this research is still in the early stages.
What are senolytic drugs, and how do they relate to longevity?
Senolytic drugs target and eliminate senescent cells, which accumulate with age and contribute to inflammation and tissue damage. By removing these cells, scientists hope to rejuvenate tissues and organs, slowing down the aging process. Also it is important to note external impacts to health .
Are there any downsides to this research?
While the research is promising, there are challenges to overcome before translating these findings into effective human therapies. The long-term effects of manipulating DNA repair mechanisms are not yet fully understood.
What if I forgot my application number?
Contact the examination authorities immediately. They can guide you with the process to retrieve it. Also, you may need to provide other information.













