18 Dead in Senegal from Rift Valley Fever | Symptoms and Risk Factors
Okay, let’s be real. Headlines about outbreaks – especially when they involve words like “dead” and unfamiliar diseases like Rift Valley Fever – can send your anxiety levels soaring. But before you spiral into a Google-fueled panic, let’s take a deep breath and break down what’s happening in Senegal, why it matters to you (even if you’re thousands of miles away), and, crucially, what you need to know to stay informed and safe. This isn’t just another news report; it’s your guide to understanding a complex situation. And maybe, just maybe, easing some of that understandable worry.
What Exactly Is Rift Valley Fever?
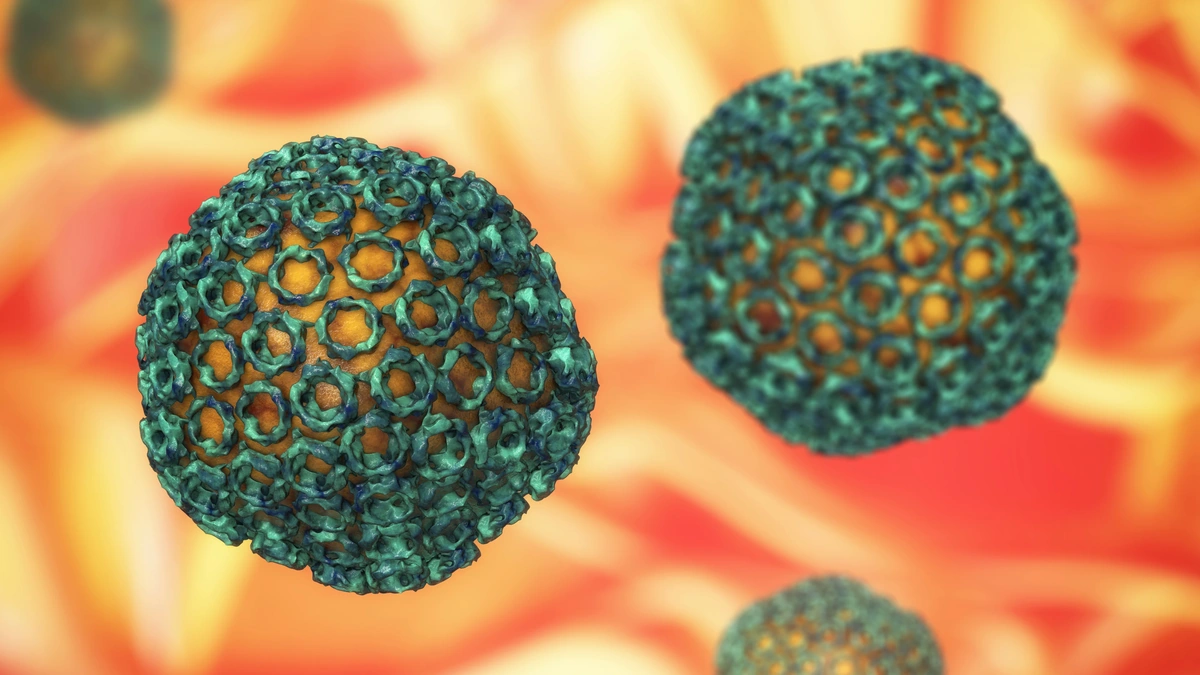
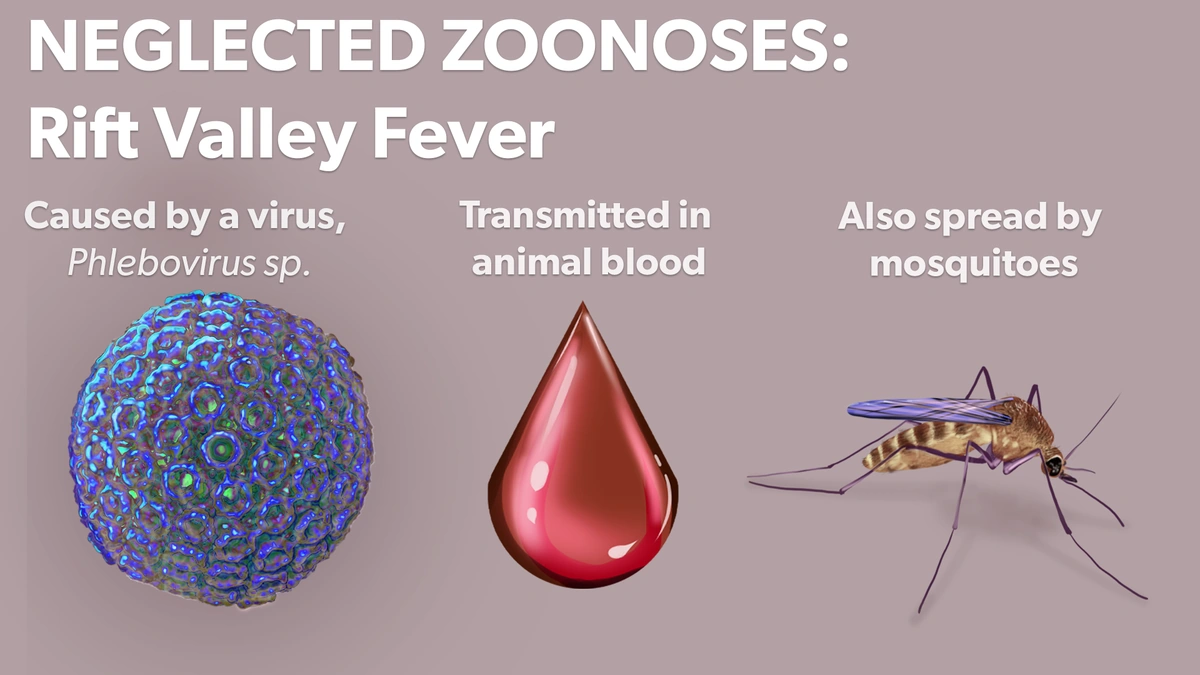
Rift Valley Fever (RVF) isn’t some brand-new, sci-fi plague. It’s been around for a while, primarily affecting animals like livestock (sheep, goats, cattle) in Africa. But here’s the kicker: it can jump to humans. We call that a zoonotic disease. The RVF virus , a member of the Phlebovirus genus, is typically transmitted through mosquito bites or contact with infected animal blood or tissues – think farmers, vets, and abattoir workers. But mosquitoes aren’t the only issue; the disease can spread through the air, and direct contact with contaminated materials. It’s a serious illness, but understanding how it spreads is the first step to prevention. Early detection is also key to controlling outbreaks and preventing severe complications. Let’s be honest, understanding the transmission routes can help in implementing targeted control measures.
Why Senegal? And Why Now?
Good question! Senegal, like many countries in sub-Saharan Africa, has a climate that’s ripe for mosquito breeding – especially after periods of heavy rainfall. The rainy season creates more breeding grounds for mosquitoes. These mosquitoes then bite infected animals and spread the virus. Several species of mosquito have been implicated. While the exact trigger for this particular outbreak is still under investigation, it’s likely a combination of environmental factors (heavy rains, flooding), animal movements, and possibly gaps in vaccination coverage for livestock. These factors can all contribute to the rapid spread of the disease.
Symptoms in Humans | What To Watch Out For
Okay, let’s get practical. If you’re in an area where RVF is present (or have recently traveled there), what should you be looking for? The symptoms can vary, but often start with flu-like symptoms. Symptoms can include:
- Fever
- Headache
- Muscle pain
- Joint pain
Sounds like a cold, right? And sometimes it is just a mild illness. But in some cases – and this is where it gets serious – RVF can lead to:
- Eye disease (retinitis) which can cause loss of vision
- Encephalitis (inflammation of the brain) leading to neurological problems
- Hemorrhagic fever (bleeding) which can be fatal
If you experience any of these symptoms, especially if you’ve been exposed to mosquitoes or livestock in an affected area, see a doctor immediately. Early diagnosis is crucial. According tothe World Health Organization, treatment is primarily supportive, focusing on managing symptoms and preventing complications.
Risk Factors | Are You At Risk?
Here’s the thing: your risk of contracting Rift Valley Fever depends heavily on your location and lifestyle. If you’re sitting in Mumbai reading this, your risk is currently very low. But if you’re a veterinarian working with livestock in Senegal, it’s a different story. Key risk factors include:
- Living or working in areas where RVF outbreaks are occurring
- Handling infected animals or their tissues
- Being bitten by infected mosquitoes
- Consuming unpasteurized milk or raw meat from infected animals
A common mistake I see people make is thinking that this is just a problem “over there.” But in our interconnected world, diseases can spread rapidly. That’s why global surveillance and early detection are so important. Travel history also plays a role; if you’ve recently visited an affected region, it’s important to inform your doctor about your travel history if you develop any symptoms.
Preventive Measures | How to Protect Yourself
Alright, let’s talk about practical steps. Even if you’re not in Senegal, understanding these measures can help you be more prepared for any potential disease outbreak. These measures can include:
- Mosquito Control: Use mosquito repellent, wear long sleeves and pants, and eliminate mosquito breeding sites around your home.
- Animal Safety: Avoid contact with sick animals. If you work with livestock, wear protective clothing and gloves. Ensure animals are properly vaccinated .
- Food Safety: Cook meat thoroughly and avoid consuming unpasteurized milk.
Let me rephrase that for clarity: It’s not just about individual actions. Public health measures, such as vector control programs and animal vaccination campaigns, are crucial for preventing and controlling outbreaks.
FAQ
Can Rift Valley Fever spread from person to person?
Person-to-person transmission is rare but possible through contact with infected blood or body fluids.
Is there a vaccine for Rift Valley Fever for humans?
There is no widely available human vaccine. However, vaccines exist for livestock.
What if I think I have Rift Valley Fever?
Seek medical attention immediately and inform your doctor about potential exposure (travel, animal contact).
How is Rift Valley Fever diagnosed?
Diagnosis involves blood tests to detect the virus or antibodies.
What’s the long-term outlook after recovering from Rift Valley Fever?
Most people recover fully, but some may experience long-term complications, such as vision problems.
Is Rift Valley Fever a global threat?
While currently concentrated in Africa, the potential for spread exists due to climate change and globalization. Surveillance is very important.
And here’s the thing: this outbreak highlights a larger issue – the increasing threat of zoonotic diseases. As the climate changes and human populations encroach on wildlife habitats, the risk of these diseases jumping from animals to humans increases. Staying informed , supporting public health initiatives, and taking simple preventive measures are all ways we can protect ourselves and our communities. So, while the news from Senegal is concerning, it’s also a reminder of the importance of global health security and proactive prevention.